In today’s whirlwind society, the allure of the “now” holds an unprecedented grip on us.
We’re living in the age of right-now convenience—from the instant magic of clicking a button to order virtually anything online, to binge-watching entire seasons of our beloved shows, or getting that quick hit of dopamine as we flip through social media.
Sure, the digital age has blessed us with a myriad of comforts. Yet, there’s a hidden price. We’ve been unknowingly conditioned to yearn for swift rewards, a pattern that might be chipping away at our productivity and undermining our chances at lasting success.
This need for instant gratification isn’t just about wanting things immediately. It’s subtly shifting our behaviors, coaxing us into more impulsive choices and muddying our decision-making waters.
But as we sail through this instant-access culture, we can’t forget the power of patience. That’s where delayed gratification steps in—the deliberate choice to skip the quick fix and hold out for something bigger and better down the road.
Stick around, because we’re diving deep into the importance of this virtue and sharing hands-on ways to master it.
Table of Contents
What Is Delayed Gratification?
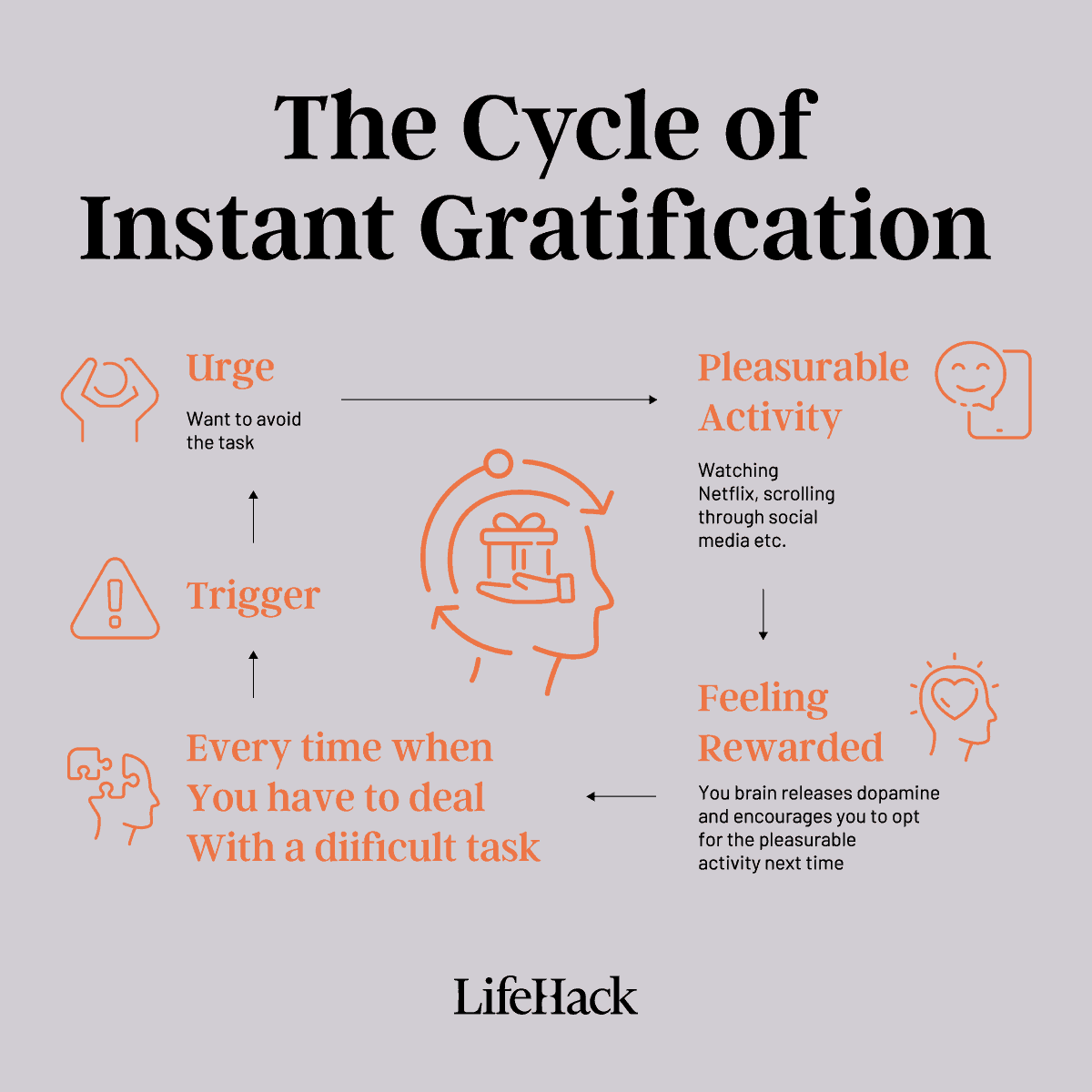
At its core, delayed gratification is all about waiting. Sounds simple, right? But, in practice, it’s like holding your breath while everyone around you is taking big, deep gulps of air. It’s the art of passing up the here-and-now goodies for something way better in the future.
Digging into the books, we see it’s rooted in the psychological realm, described as the knack to sideline an immediate prize for a more rewarding one later on.[1] Some folks dub it as impulse control or self-control.
To peel back another layer, let’s talk about the “Pleasure Principle.”[2] Coined by the renowned Sigmund Freud, it boils down to this:
We humans have this natural urge to chase pleasure pronto and dodge pain. It’s like our inner software programmed to want instant fixes—be it quenching thirst or grabbing a bite.
Makes sense in some situations, right? But in today’s maze of choices, sticking to this instant-pleasure mode can steer us into hasty, short-sighted actions. Think munching on that extra cookie instead of staying true to a fitness regime.
Let’s paint a clearer picture. Delayed gratification plays out in daily scenes:
- It’s choosing a power-packed salad over a fast-food fix, keeping our health in check and chasing those fitness milestones.
- It’s about resisting that flashy sale, stashing away some cash, and focusing on long-haul financial dreams.
- Think of it as picking a challenging project, networking, or learning something new, even if it means skipping today’s Netflix binge. The end game? Career wins.
- And it’s the decision to close that game or pause that TV show, hitting the books instead, and chasing academic excellence.
Now, here’s a personal slice of pie from us:
Years back, we, too, got lured by the siren call of instant rewards. We were in the business of churning articles, and our compass was pointing straight at social media approval—those sweet likes and shares.
But here’s the hiccup: in chasing the quick applause of digital thumbs-ups, we veered off our actual path—empowering people to flourish and boost their productivity.
Instead of dropping knowledge bombs that could potentially change lives, we were in the race to be the trendiest.
We had to pivot. So, we took a breath, pressed reset, and started focusing on quality over quick wins. Even if it meant fewer likes, we wanted our words to be the wind beneath our readers’ wings.
End of the day, this switch was gold. Staying faithful to our essence, we’ve built a tribe of folks who are as stoked about productivity as we are. And that, is the power of playing the long game.
The Power of Delaying Gratification
Let’s get something straight: holding off on what you want right now isn’t about depriving yourself. It’s about gearing up for something even better down the line.
When you hit pause on that immediate urge, you’re flexing a special kind of muscle called self-control, setting yourself up for some fantastic future rewards.[3]
People who’ve got this self-control thing down are setting their sights on the horizon. They’re all about the big picture, which means they’re ticking off goals and riding high on the satisfaction wave.
Short-lived temptations? Nah, they’re all about chasing those game-changing, feel-good victories.
Greater Success
Think of delayed gratification as your personal trainer for willpower. It’s coaching you to plant your eyes on what truly counts and to shrug off those shiny distractions.
Remember the legendary “marshmallow experiment”?[4] Back in ’72, psychologist Walter Mischel rolled out this simple test. Kids had a choice: snag one marshmallow now or wait it out a bit for double the treat.
Fast forward, and here’s the twist: those patient kiddos who waited for the two marshmallows? They were smashing it in life—stellar grades, keeping their emotions in check, and just generally winning at the life game.
Improved Health
Here’s another feather in delayed gratification’s cap—it’s a health booster. You’re more likely to make those health-smart choices, like passing up that greasy snack or lacing up for a workout.
And it’s not just about the body.[5] It’s about leveling up emotionally. Holding off on snap reactions means you’re navigating feelings like a pro, sidestepping drama, and building rock-solid relationships.[6]
Boost Your Self-Worth and Confidence
But wait, there’s more. Every time you practice patience, you’re sharpening your sense of self-efficacy—that rock-solid belief that you’ve got what it takes.
You’re not just sitting around; you’re dodging curveballs and tapping into that deep well of resilience. And when you see the fruits of your patience? Confidence boost.
So, next time you’re faced with that “want it now” moment, just remember: hitting the pause button isn’t about missing out. It’s about setting up for something epic.
Because good things? They come to those who wait.
How to Delay Gratification
Delaying that urge, that instant “I-want-it-now” feeling? It’s a skill, and the good news is, you can totally get better at it.[7]
Let’s dive into some practical ways to up your game:
1. The Time Flow System: Your Blueprint
Developed by me and my LifeHack team, the Time Flow System is like a GPS for your goals:
- North Stars: These are your big dreams, guiding your journey.
- Initiatives: These are the steps making sure you’re on track.
- Focus Blocks: This is your time shield, keeping you locked in.
Here’s a breakdown:
I. Identify Your North Stars
What’s your big dream? You need to see it, breathe it. When you’ve got that North Star shining bright in your mind, you’re less likely to get side-tracked by little detours.
Picture your win – the celebration, the thrill. That’s the energy you tap into when the right-now shiny stuff tries to woo you.
II. Break Down Challenges into Doable Tasks
Huge task got you freaked? Chop it up! Slice that monster into smaller chunks. Suddenly, that scary beast looks a lot friendlier.
These chunks? They’re your Initiatives leading you straight to your North Star.
Stuck on the slicing? No worries, there’s a guide for that.
III. Eliminate Temptations
are sneaky. They’re always lurking. But you can outsmart them.
Block out time – that’s your Focus Block. It keeps you zoned in on what matters. This way, you’re always marching toward your North Star, taking the right steps.
You can learn more about the Time Flow System here.
2. Celebrate Small Wins
Think of it as giving yourself a high-five. Every step forward, no matter how tiny? It’s a win.
Revel in it. These little boosts keep the energy up and remind you that, hey, you’re making progress.
Need some inspo to get your celebration on? Here’s a peek.
3. Practice Mindfulness
Now, here’s a superpower: mindfulness. It’s like tuning in to a radio frequency where you can hear yourself loud and clear.[8] It’s about being in the moment, understanding those impulses, and making choices that truly resonate with where you want to go.
Stress, mood swings, those urgent cravings – they often pull the instant gratification trigger. With mindfulness, you can keep that trigger in check, breathe through the chaos, and choose your response.
Dive deep into mindfulness with these beginner tips, meditative practices, and my personal favorite, deep breathing exercises. Trust me, 15 minutes a day, and you’ll feel the difference.
Final Thoughts
Think about it: Holding off on that splurge today can mean a stable bank account tomorrow. Waiting a bit before reacting can turn a heated chat into a meaningful conversation. And those big dreams? Well, they often ask for a bit of waiting and working through the small stuff first.
Delaying gratification isn’t just about putting things off. It’s about making smarter choices—choices that echo who you really are and where you genuinely want to go. It’s like having a compass in the maze of life.
With delayed gratification, you’re not wandering around; you’re on a path, a journey with purpose.
Master the art of waiting in those small moments, and you’ll find yourself ready for the bigger challenges.
Reference
| [1] | ^ | Britannica: delay of gratification |
| [2] | ^ | American Psychological Association: Pleasure Principle |
| [3] | ^ | Sage Journal: Good Things Come to Those Who Wait: Delaying Gratification Likely Does Matter for Later Achievement (A Commentary on Watts, Duncan, & Quan, 2018) |
| [4] | ^ | American Psychological Association: Acing the marshmallow test |
| [5] | ^ | American Psychological Association: What you need to know about willpower: The psychological science of self-control — Willpower and healthy behaviors |
| [6] | ^ | J Appl Dev Psychol.: Physiological Profiles During Delay of Gratification: Associations with Emotionality, Self-regulation, and Adjustment Problems |
| [7] | ^ | Science Advances: The neural basis of delayed gratification |
| [8] | ^ | Frontiers in Human Neuroscience: Self-awareness, self-regulation, and self-transcendence (S-ART): a framework for understanding the neurobiological mechanisms of mindfulness |