Have you noticed how, in our modern era, we’ve unknowingly trained ourselves to crave immediate rewards?
Think about it. With a mere click, we’re ordering meals, buying gadgets, or checking how many people “liked” our latest photo. We’re living in an age where waiting feels almost unnatural.
But this need for now, this expectation for things to happen in the blink of an eye, has its drawbacks. It’s making us restless, lowering our tolerance for any delay.
And the more we cave into this urge, the more we risk our potential for success, both in our personal lives and our careers.
Dive into this article to understand the depths of instant gratification and how it might be pulling the brakes on your ambitions.
Table of Contents
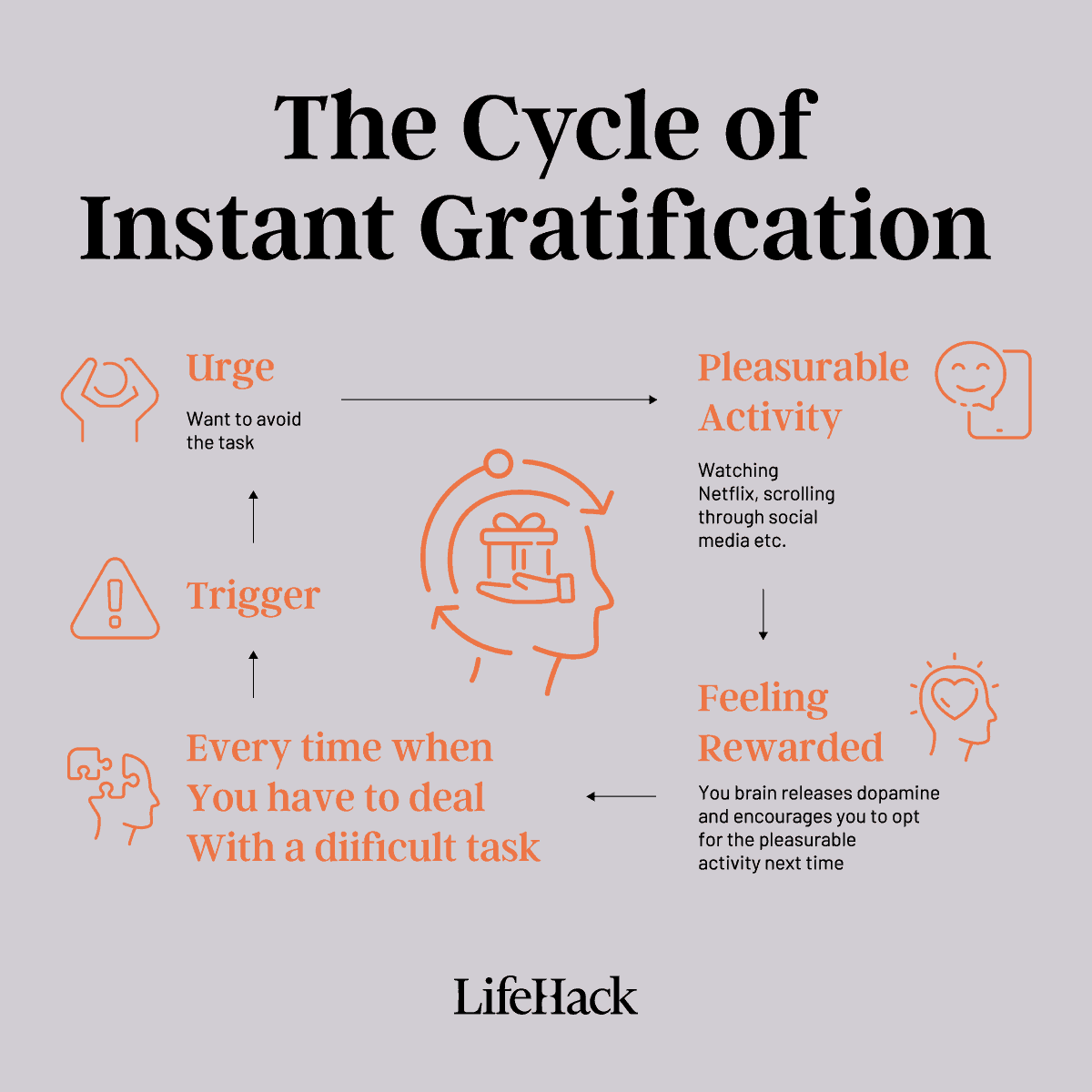
Instant Gratification in a Nutshell
So, what exactly is this “instant gratification” we keep talking about?
In simple terms, it’s our itch for quick pleasure. It’s that urge to get what we want right now without waiting or putting in effort. It’s choosing the short-term win, even if it means ignoring what might be better for us in the long run.
This whole phenomenon isn’t new. In fact, Sigmund Freud, a big shot in the world of psychology, had a name for it: the “Pleasure Principle.”[1] In his eyes, we humans are driven by a desire to feel good, and feel good quickly.
Let’s get real with an example.
My son? Big chess enthusiast. He’s in a chess club, works hard with a coach, and immerses himself in chess strategies.
But not too long ago, he got super frustrated. He kept losing games to his coach and wanted to throw in the towel. Just walk away.
Now, if he’d acted on that impulse, wanting to dodge the discomfort and look for a quick out, he’d have been giving in to instant gratification. He’d miss out on the kind of practice that would actually make him better.
To steer him away from that, I suggested a breather. “Step back, refocus, then get back to the game,” I said.
His coach pitched in too, breaking their sessions into bite-sized challenges. It made grasping strategies a tad easier.
But hey, it’s not just kids. Adults? Oh, we’re big culprits too. Think about these:
- That buzz you feel when your photo on social media gets likes or comments? That’s you riding the instant gratification wave.
- Those moments when you know you should eat healthily, but that fast food burger calls out? Yep, the siren song of immediate pleasure.
- Ever had something significant to do but found yourself aimlessly scrolling online or binge-watching? That’s the lure of the ‘now’ over what truly matters.
If any of that rings a bell, then like many of us, you’ve got a silent guest in your life: instant gratification.
Why Are We Drawn to Instant Gratification?
Why does that candy bar seem so tempting? Why does the ‘like’ notification on your post bring such a rush?
If you’ve ever wondered why we’re so easily seduced by the ‘here and now,’ you’re not alone.
Let’s peel back the layers and dive into why instant gratification feels like second nature:
Blame It on Our Brain
It starts with us, the people. Deep down in our biological wiring, our brains are on the hunt for pleasure and on the run from pain—thanks to the “Pleasure Principle.”
This isn’t some modern-day quirk; it’s been with us since our baby days.[2] When we scratch that itch, our brain rewards us by releasing dopamine, giving us that happy feeling.
On the flip side, when we don’t get what we want, we feel uneasy, restless. Holding back isn’t fun. So, naturally, we tend to grab any feel-good chance we spot.
Tech Isn’t Helping
Then there’s the world around us. Our gadgets, apps, and ever-speedy internet. Everything’s on tap, right from messages to media, urging us to get things now.[3]
And let’s talk about social media. It’s turned us into ‘like’ addicts. A comment here, a share there, and we’re on cloud nine.[4]
With every ding and notification, our craving for that immediate thumbs-up just grows.
Life’s Curveballs
Lastly, let’s face it: life’s been a rollercoaster. Think pandemics, global tensions, and other curveballs that make tomorrow seem murky. In such times, we tend to think short.
Why wait for a maybe when there’s a sure-shot ‘good’ right now? Whether it’s digging into a tub of ice cream or binging that new series, it’s all about getting that quick mood boost when everything else feels uncertain.
So, there you have it. It’s a mix of our brains, the tech-savvy world we live in, and the unpredictability of life that keeps pulling us towards the instant, often at the cost of the enduring.
The Real Issue of Instant Gratification
We live in a world where a double-tap can fetch likes, a two-minute microwave ding promises a hot meal, and the promise of ‘next-day delivery’ is now ‘same-day delivery.’
And while these quick fixes might offer us fleeting joy, there’s a hidden cost we often overlook: the long-haul win.
Instant gratification might sound and feel good in the moment, but it could be steering you away from the bigger picture. Here’s why:
Caught in the Loop of Tomorrow
You’ve been there—choosing another episode over that assignment or scrolling endlessly when you should be preparing for that presentation. This lure of the ‘right now’ can pull us into a procrastination loop.
When we constantly pick momentary delights, we’re shelving what truly matters. This cycle of putting things off not only chips away at our productivity but also cranks up our stress levels, especially when deadlines loom large.
And here’s the catch: the more you fall for the ‘instant,’ the tougher it gets to snap out of it. It’s like quicksand—the more you wiggle, the deeper you sink, often into feelings of guilt and anxiety.
Watching Dreams Slip By
Chasing the ‘now’ reprograms your brain. It starts wanting every reward pronto, sidelining your larger dreams that require grit, patience, and time.
And there’s research to back this up. When we give in to the moment, our willpower wanes, making it even harder to resist the next temptation.[5] Before you know it, your self-control’s taken a hit, and big dreams seem more like distant fantasies.[6]
There’s this famous experiment, the Marshmallow Test. Kids could either munch one marshmallow immediately or wait a bit and get two. Fast forward, and those who held back, aiming for the bigger prize, turned out to fare better in life’s many tests, from academics to health.[7]
It’s a simple lesson – resist the small and immediate, and you set yourself up for bigger, long-lasting rewards.
The Speed Trap
Let’s talk about our shrinking patience. The more we’re served on a platter instantly, the less patient we become—expecting everything, from career growth to love, at lightning speed.
Think about this quote by Sam Owen, the author of Resilient Me:
“We’re becoming impatient and lazy and we’re allowing this to shape our approach to our relationships. But successful relationships aren’t handed over on a plate, or downloaded at the click of a button, or ours in twenty-four hours for just £9.99 extra. Relationships are up there with food, water, clothing and shelter and you can’t just buy them or trade them in for an upgrade.”
When this ‘speed-demand’ creeps into our relationships, we’re setting ourselves up for rocky times.
A small disagreement? Our dwindling patience could magnify it. Challenges? We might be too hasty to walk away.
And it’s not just relationships—it’s our choices. We might leap before we look, leading to regrettable decisions.
While the ‘now’ might look tempting, it’s wise to sometimes choose the ‘later.’ Because the bigger joys often lie a bit further down the road.
How to Delay Gratification For Good
The world zips by with instant ‘everything’—but what if the secret to success lies in pressing ‘pause’? Well, it does.
Delaying gratification isn’t just about turning down that extra cookie; it’s a power move for life. It’s a skill, and the good news is, just like learning to ride a bike, it can be mastered.[8]
Here’s a quick guide on how you can harness the power of waiting:
1. Spotlight on the Prize
First, figure out your ‘why.’ Why resist the lure of the ‘now’?
If you can visualize where you want to be in a year, five years, or even a decade, you’ve got your map.
Think of this as your North Star—a bright, shining goal that’ll guide you on those tricky turns.
2. Out of Sight, Out of Mind
Distractions are sneaky. One minute you’re working, the next, you’ve lost an hour to cute animal videos.
Use technology to your advantage. There are tons of apps and tools designed to keep distractions at bay. The Time Flow System app is one of them, developed by the LifeHack Team, to help you schedule “Focus Blocks” to stay focused on important stuff that needs to be done. Find out more about the Time Flow System here.
Block the noise, set your boundaries, and stay on track.
3. Slice it Up
Staring at a mountainous task can be daunting. But what if you broke it down into hills?
Chunking down challenges makes them more approachable. Instead of feeling overwhelmed, you’ll feel empowered, piece by piece.
4. Celebrate the Journey
Remember, every step counts. When you hit a mini-goal, give yourself a pat on the back.
These moments of recognition fuel your motivation, making the journey feel just as rewarding as the destination.
5. Stay Present
This isn’t about meditation (though that helps). It’s about being in the moment.
With mindfulness, you can understand your impulses and navigate them. It’s your internal compass, helping you stay aligned with your goals.
For a deep dive, don’t miss out on How to Use Delayed Gratification to Your Advantage. It’s packed with insights and tools to master the art of waiting.
In the race of life, sometimes slowing down gives you the ultimate edge. Remember, it’s the long game that counts.
Final Thoughts
Diving headfirst into the pool of instant gratification feels good in the moment. It’s a quick hit of happiness. But, over time, it might just keep us from the big wins in life. When we’re always chasing the ‘now,’ we might miss the magic of ‘later’.
To really thrive, we need to play the long game. That means having grit, patience, and the vision to say ‘no’ to the immediate in favor of the future’s ‘yes’.
And the biggest win? The ability to wait isn’t locked in our DNA; it’s a skill. With a bit of effort, we can get better at it.
By training ourselves to look ahead and resist the urge for the quick fix, we’re setting ourselves up not just for success but for a life rich with purpose and meaning.
It’s not always the easy path, but it’s certainly the one with the better view at the end.
Reference
| [1] | ^ | APA Dictionary of Psychology: Pleasure Principle |
| [2] | ^ | Scientific Reports: Infant expectations of instant or delayed gratification |
| [3] | ^ | The University of Alabama: I WANT IT NOW: DO NEW MEDIA AFFECT ABILITY TO DELAY GRATIFICATION? |
| [4] | ^ | Elliot Panek, University of Alabama: Immediate Media: How Instant Gratification, Self-Control, and the Expansion of Media Choice Affect our Everyday Lives. |
| [5] | ^ | American Psychological Association: What you need to know about willpower: The psychological science of self-control |
| [6] | ^ | nesslabs: Present bias: how instant gratification impacts your long-term goals |
| [7] | ^ | J Pers Soc Psychol.: Cognitive and attentional mechanisms in delay of gratification |
| [8] | ^ | Science Advances: The neural basis of delayed gratification |