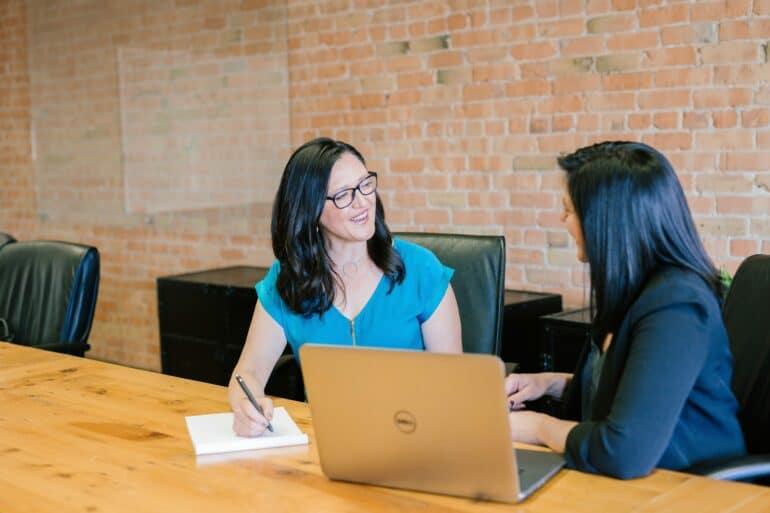
Dark chocolate is certainly a delicious treat. But did you know that for centuries, dark chocolate has long been associated with health benefits?
Incas referred to a beverage made from cocoa as “the drink of the gods,” which eventually gave rise to its scientific name Theobroma cacoa, derived from the Greek words theo (god) and broma (drink). Aztec Emperor Montezuma stated that cocoa “builds up resistance and fights fatigue” and can “permit a man to walk for a whole day without food.”
While it seems almost too good to be true, the health benefits to eating a moderate amount of dark chocolate are backed by science. Let’s dive right into the health benefits of dark chocolate.
13 Health Benefits of Dark Chocolate
1. Full of Nutrients
A small bar of 70-85% dark chocolate, let’s say 50 grams/1.75 ounces, contains
- nearly 6 grams of fiber for digestive health
- a third of your recommended daily allowance (RDA) for iron to promote cardiovascular fitness
- over a quarter of your RDA for magnesium for skeletal health
- nearly 50% of your RDA for copper and manganese, important for antioxidant functions
It is also important to note that a serving of dark chocolate contains 300 calories, so it is best to consume dark chocolate in moderation.
And don’t worry! You can still get these healthy effects from smaller servings; just try to make sure you are eating dark chocolate that is 70-90% cocoa.
2. Protect You from Inflammation
Dark chocolate is rich in a class of phytonutrients called flavonoids,[1] which are one of the most common and largest groups of phytonutrients found in the diet.
These phytonutrients are chemicals found in plants that promote health. They help protect our bodies from damaging harmful free radicals that can lead to inflammation and diseases like diabetes, cancer and Alzheimer’s disease.[2]
3. Help Lower Blood Pressure
Dark chocolate and cocoa contain specific flavonoids called flavan-3-ols (or flavanols). Flavan-3-ols/flavonols can lower blood pressure. Research has shown that after consumption of dark chocolate, antioxidant capacity in blood increased, which led to the opening of blood vessels and decreased blood pressure.[3]
4. Decrease “Bad” Cholesterol and Increases “Good” Cholesterol Levels
Cholesterol is made up of low-density lipoprotein (LDL), high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL). LDL is considered the “bad” cholesterol that can build up on the walls of arteries, while “HDL” is called the good cholesterol, which can block LDL from building up on arteries.
A variety of studies have shown that both dark chocolate and cocoa powder reduced LDL and oxidized LDL levels and increased HDL levels.[4][5]
5. Reduce Platelet Aggregation
Platelets are components found in blood cells that help to form clots. While clots are critical in stopping excessive bleeding, hyperactive platelets can contribute to coronary heart disease.
A study investigating the effects of white, milk, or dark chocolate showed that dark chocolate inhibited platelet accumulation, while white and milk chocolate had no effect on platelet clustering.[6]
6. Reduce the Risk for Cardiovascular Disease
A study[7] researching the long-term diet habits in nearly 500 elderly men revealed that cocoa intake was inversely correlated with cardiovascular disease and mortality rates that were assessed 15 years after the study began.
Another epidemiological study in the US general population demonstrated that consumption of chocolate was inversely related to coronary heart disease and that eating chocolate 5 times per week lowered the coronary heart disease risk by 57%.[8] So go ahead and enjoy a daily piece of dark chocolate!
7. Help Lower the Risk for Stroke
An analysis, published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition,[9] of five different studies demonstrated a nearly 20% stroke risk reduction when comparing those defined as high consumers (~ 62.9 grams/week or a tenth of a pound for our non-metric friends out there) to those defined as low consumers of dark chocolate (~ 0 grams/week).
8. Help Reduce Insulin Blood Sugar Spikes
The same study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition with an analysis of over 40 clinical trials, including nearly 1300 participants, found that nutritional interventions with cocoa or chocolate significantly reduced fasting insulin concentrations and insulin resistance, endpoints which are used to assess risk for the development of diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Again, moderation is key here and the distinction between cocoa/dark chocolate and milk/white chocolate is critical since milk/white chocolate have lower levels of healthful components.
9. Improve Cognitive Function
A 450 milligram dose (about 1/6 of a teaspoon) of cocoa flavanols increased cerebral blood flow to gray matter in the brain. Additionally, a five day regimen of 150 milligrams of cocoa flavanols increased blood oxygenation levels.[10]
In addition, a study[11] in 90 elderly participants investigated the effects of a high (~990 milligrams), intermediate (~520 milligrams), or low (~45 milligrams) cocoa flavanol doses.
Researchers found that participants on the high flavanol track were able to complete cognitive tests much faster and scored better on verbal fluency test scores in comparison to those assigned to low flavanol supplementation. That means, dark chocolate could make you smarter.
10. Reduces Stress
Preliminary studies[12] demonstrate that dark chocolate consumption reduced excretion of cortisol and catecholamines, hormones involved in the body’s stress response.
Other researchers have shown that consumption of dark chocolate buffered stress responses and reduced levels of perceived stress as assessed through a stress questionnaire.[13]
Now it makes even more sense to keep a bar of dark chocolate at work.
11. Boost Energy
Dark chocolate contains a small amount of caffeine – two ounces of 70% dark chocolate contains about 50-60 mg caffeine.[14]
So, if you’re looking for an alternative pick-me-up to your traditional afternoon cup of coffee, dark chocolate is a nice option.
12. Help Protect the Skin
Consumption of flavanol rich chocolate protects against UV rays by increasing the minimum amount of UV rays required to cause skin redness.[15]
Moreover, flavanols from cocoa improve blood flow to the skin and increase skin hydration and thickness.[16]
13. Help Improve Teeth Health
Dark chocolate is rich in the antioxidant theobromine, which has been shown to protect the enamel surfaces of teeth.[17] This potent antioxidant is better than fluoride at remineralizing and hardening tooth enamel.
But again, moderate consumption is key.
Bottom Line
Dark chocolate has proven to be a great compliment to a healthy diet, thanks to its high antioxidant content and potential role in lowering the risk of heart disease. Its capacity to improve mood, cognitive function, and overall well-being solidifies its reputation as a delectable treat with genuine health benefits.
Keep in mind to consume it in moderation and choose the kinds with a high cocoa content in order to reap the health benefits of dark chocolate.
Featured photo credit: Towfiqu barbhuiya via unsplash.com